Uncategorized
Unlock CPU Power Settings in BIOS on Windows 11 for Optimal Performance
If you’re looking to push your Windows 11 system to its peak performance, optimizing your CPU settings through BIOS can make a significant difference. Overclocking, adjusting power settings, and fine-tuning other CPU parameters can unlock the true potential of your processor, enabling smoother performance and faster processing speeds. However, modifying these settings without a solid understanding can lead to system instability, overheating, and even hardware damage. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to accessing and adjusting CPU power settings in BIOS on Windows 11 safely and efficiently.
What is BIOS, and Why Adjust CPU Power Settings in Windows 11?
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is an essential firmware that initializes hardware components and prepares your PC to run the operating system. Unlike software adjustments that can be limited in scope, accessing the BIOS allows for more direct control over your CPU and other hardware.
In Windows 11, accessing BIOS to unlock CPU power settings can:
- Increase the processor’s operating frequency, boosting overall speed.
- Optimize power consumption and enhance energy efficiency.
- Improve system stability when running demanding applications.
Fine-tuning the CPU power settings through BIOS can be particularly advantageous for users running resource-heavy software, such as video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming applications. Let’s dive into the steps and best practices for adjusting these settings.
Accessing BIOS in Windows 11
Step 1: Enter BIOS Settings
To unlock CPU power settings in BIOS on Windows 11, you must first access the BIOS interface. Here’s how:
- Restart your PC: Click on the Start button, select the Power icon, and choose Restart.
- Press the BIOS Key: As the system restarts, continuously press the specific BIOS key for your device (usually F2, F10, DEL, or ESC). The exact key can vary depending on your device manufacturer, so check your motherboard’s manual if needed.
- Enter Advanced Mode: Once in the BIOS, navigate to the Advanced Mode (often accessible by pressing F7 or via a designated tab). Advanced Mode provides access to more detailed CPU and system settings.
Note: Exercise caution when modifying BIOS settings. Incorrect configurations can impact system stability.
Step 2: Locate CPU Power Settings
In the BIOS interface, the CPU settings are typically located under tabs labeled as Performance, CPU Configuration, Overclocking, or Advanced Frequency Settings. This is where you can adjust various CPU settings, including voltage, frequency, and power management options.
When you unlock CPU power settings in BIOS on Windows 11, you open up several adjustment options:
- CPU Frequency: Determines the operating speed of the CPU. Increasing the frequency can enhance processing speed but also increases power consumption and heat output.
- CPU Core Voltage: Adjusting core voltage controls the amount of power supplied to the CPU. Higher voltage can support higher frequencies, but it also increases heat.
- Power Limit Settings: The Power Limit controls the maximum power the CPU can draw. Adjusting this setting helps to maximize performance without overheating.
Key Settings for CPU Optimization in BIOS
1. CPU Frequency and Ratio Multiplier
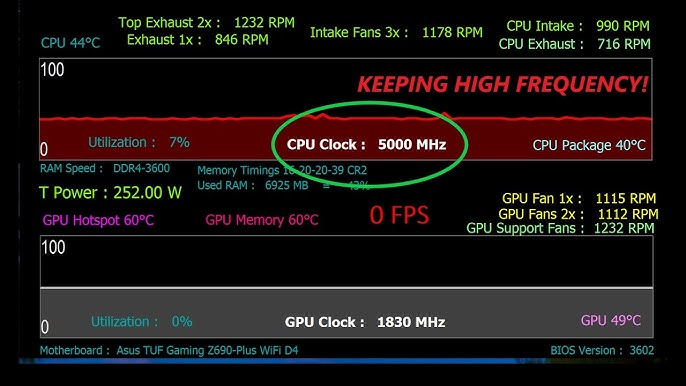
Adjusting the CPU ratio multiplier allows you to increase your CPU’s clock speed. For instance, if your base clock speed is 100 MHz and you set a multiplier of 40, your CPU will operate at 4 GHz.
- To Adjust CPU Frequency:
- Locate the CPU Ratio setting in BIOS.
- Increase the multiplier incrementally (e.g., by one or two points at a time).
- Test system stability with each increase to ensure no crashes or overheating.
2. Voltage Control
Voltage adjustments are critical for overclocking but must be handled with care. Increasing voltage helps sustain higher CPU speeds but can lead to higher temperatures. Some CPUs have a specific “safe voltage range,” which should not be exceeded to avoid thermal issues or hardware damage.
- Adjusting CPU Voltage:
- Navigate to the CPU Core Voltage setting.
- Increase voltage in small increments (e.g., 0.01V).
- After each adjustment, monitor temperatures using BIOS or third-party software.

3. Thermal Controls
Thermal controls, such as CPU fan speeds and temperature thresholds, are essential to prevent overheating. By configuring these settings, you can manage the cooling system more effectively, ensuring that your CPU remains within safe temperature limits.
- Setting Fan Speed Profiles:
- Find the Fan Speed Control settings in BIOS.
- Set a custom fan speed curve to increase fan speed as temperature rises.
- Choose higher fan speeds for better cooling during intensive tasks, but balance for noise control.
Unlocking Advanced Power Settings
For users with high-performance needs, some motherboards offer additional settings in BIOS that allow further power customization.
1. Power Limit (PL1 and PL2)
- PL1 (Long Duration Power Limit): This setting defines the power level the CPU can sustain for extended periods. Increasing PL1 allows for more consistent high performance.
- PL2 (Short Duration Power Limit): This setting determines the power the CPU can use for short bursts. Increasing PL2 enables brief, higher performance for demanding applications.
2. Load-Line Calibration (LLC)
Load-Line Calibration helps stabilize CPU voltage during heavy workloads, reducing voltage drop. This can improve stability, especially when overclocking.
- Setting Load-Line Calibration:
- Go to Voltage Settings or Power Management.
- Adjust the LLC level incrementally to stabilize voltage without over-compensating.
Tip: Only adjust LLC if you experience voltage instability during demanding tasks.
Best Practices for Adjusting CPU Settings
When you unlock CPU power settings in BIOS on Windows 11, it’s essential to follow best practices to avoid system instability. Here are key tips for safe and effective CPU tuning:
- Incremental Adjustments: Make changes in small increments. Drastic adjustments to frequency or voltage can lead to crashes or hardware issues.
- Test System Stability: After each change, test your system using benchmarking software like Prime95, Cinebench, or AIDA64 to ensure stable performance.
- Monitor Temperatures: High temperatures can damage your CPU. Use monitoring software to keep track of CPU temperature and ensure it stays within safe limits.
- Enable Thermal Throttling: Most modern CPUs have built-in thermal throttling. Ensure this feature is enabled to prevent overheating.
Risks and Considerations
While unlocking CPU power settings in BIOS on Windows 11 offers performance benefits, it’s not without risks. Overclocking can void warranties, and incorrect configurations may damage your CPU or motherboard. Always research your specific CPU and motherboard capabilities and consult documentation to understand limitations.
FAQs
Yes, you can access BIOS on any Windows 11 PC, although the method to enter BIOS may vary based on your motherboard and manufacturer. Generally, pressing F2, DEL, or ESC during boot-up works for most systems.
BIOS and UEFI are both firmware interfaces. UEFI is a more modern version of BIOS with advanced features like support for larger hard drives and faster boot times. Many new motherboards feature UEFI instead of traditional BIOS.
In some cases, overclocking or modifying CPU settings may void the warranty. Always consult your warranty terms and conditions before making significant changes.
You can use third-party software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or MSI Afterburner to monitor CPU temperature in real time and ensure your settings are safe.
Increasing CPU voltage can lead to higher temperatures, which may shorten the CPU’s lifespan if it frequently operates above recommended temperatures. Incremental adjustments and temperature monitoring are crucial.
Unlocking CPU power settings in BIOS on Windows 11 can elevate your system’s capabilities and allow for more seamless performance in demanding applications. Follow these guidelines to maximize your CPU’s potential safely, test your settings rigorously, and monitor performance closely for an optimized computing experience.