Uncategorized
Set CPU Frequency Limits in BIOS: Windows 11 Guide
Setting CPU frequency limits in the BIOS is an effective way to control power consumption, manage heat, and maintain system stability, especially for users looking to optimize their Windows 11 experience. Adjusting CPU frequency at the BIOS level ensures that your changes are applied before the operating system even loads, offering a hardware-level solution for controlling performance. In this guide, we’ll walk you through configuring BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility settings to help you safely and effectively optimize your system.
Why Set CPU Frequency Limits in BIOS?
Configuring CPU frequency limits in the BIOS provides several key benefits:
- Power Efficiency: Lowering CPU frequency can save power, especially useful for laptops or power-sensitive applications.
- Heat Management: Reducing CPU speed helps to keep system temperatures lower, preventing overheating and extending hardware lifespan.
- Stability in Resource-Intensive Applications: By setting a safe maximum frequency, you can prevent sudden performance drops or system throttling during heavy tasks.
Setting limits at the BIOS level ensures a stable baseline configuration for Windows 11, making it compatible with various workloads while managing resources effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Set CPU Frequency Limits in BIOS for Windows 11
The process of setting CPU frequency limits in BIOS will vary slightly based on the motherboard manufacturer, but the steps below provide a general guideline.
Step 1: Access the BIOS on Windows 11
- Restart Your Computer: Begin by shutting down or restarting your computer.
- Enter BIOS Setup: As the computer boots, press the designated key to enter BIOS. This key varies by manufacturer (commonly
F2,Del, orF10). - Find the BIOS Settings: Once in the BIOS interface, navigate through the options using the arrow keys.
Entering BIOS provides direct access to CPU configuration settings, enabling you to set a BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility tailored to your needs.
Step 2: Locate the CPU Frequency Settings
Once in the BIOS, locate the settings related to CPU performance:
- Navigate to the Advanced Settings: Look for a section labeled Advanced or Overclocking. The CPU settings may also be under Performance or Power Management, depending on the BIOS.
- Find CPU Frequency Settings: Look for terms like CPU Frequency, CPU Multiplier, or Core Ratio. These options allow you to adjust how fast your CPU operates.
- Identify Frequency Limits: You may see a “maximum” or “multiplier” value that determines the upper limit of your CPU’s speed.
Each BIOS interface is unique, so if you’re unsure, consult your motherboard manual or online documentation specific to your model.
Step 3: Set a CPU Frequency Limit
Now that you’ve found the relevant settings, it’s time to set the CPU frequency limit.
- Adjust the CPU Multiplier: CPU frequency is often controlled by a multiplier setting. For instance, if the CPU base clock is 100 MHz and the multiplier is set to 35, the resulting frequency is 3.5 GHz (100 MHz x 35).
- Reduce the Multiplier to Lower the Limit: Lowering the multiplier will reduce the CPU’s maximum operating speed. For example, setting the multiplier to 30 limits the CPU to 3.0 GHz.
- Save Your Changes: Once you’re satisfied with the settings, save and exit the BIOS. This step may be labeled as Save & Exit or Apply Changes.
Setting a BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility at a conservative level is a practical approach for balancing performance and power consumption without sacrificing stability.
Step 4: Test Your New CPU Frequency Limit in Windows 11
After setting the CPU frequency limit, it’s essential to verify that the changes have improved system stability without causing performance issues.
- Monitor CPU Performance: Use tools like Task Manager or third-party software (e.g., HWMonitor, CPU-Z) to monitor the CPU’s frequency and ensure it aligns with your BIOS settings.
- Run System Stability Tests: Run resource-intensive applications or benchmarks to confirm that the new frequency limit does not lead to unexpected crashes or system instability.
- Evaluate System Temperature: Monitor your system’s temperature while under load to ensure the CPU limit has a positive effect on reducing heat.
Testing your settings within Windows 11 confirms that your BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility adjustments have been successful without compromising usability.
Advanced BIOS Settings for CPU Frequency Control
If you’re comfortable with advanced configurations, additional BIOS options can help you fine-tune your CPU performance even further.
Step 5: Use Turbo Boost and Power Limits
Some CPUs, especially Intel models, have Turbo Boost or similar technology that temporarily increases CPU frequency when extra power is needed. Managing these settings can help keep CPU usage under control.
- Disable or Adjust Turbo Boost: In the BIOS, look for options labeled Turbo Boost or Boost Mode. Disabling or limiting this feature can prevent short bursts of high CPU frequency.
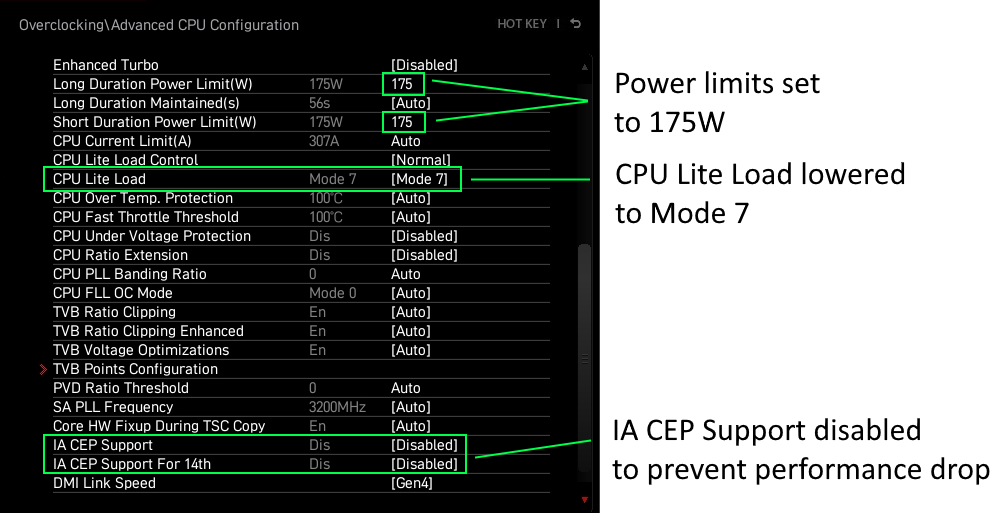
- Set Power Limits: Some BIOS configurations allow you to set power limits (PL1, PL2) for the CPU, which caps how much power the CPU can draw, effectively limiting its maximum frequency.

Controlling Turbo Boost and power limits is another effective way to maintain BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility, particularly for systems that prioritize stability and power efficiency.
Step 6: Enable Core Parking
Core Parking controls which CPU cores are active and can be configured in some BIOS versions to help save power.
- Locate Core Parking Settings: In the Advanced CPU Configuration section, look for options related to Core Parking or Core Activation.
- Enable Core Parking: Enabling Core Parking allows the system to deactivate cores when they’re not in use, reducing overall power consumption and heat.
- Save and Exit BIOS: Apply the settings and exit BIOS to implement core parking.
Core Parking is particularly useful for mobile devices or laptops where battery life is a priority, and it works well with BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility settings.
Step 7: Set Voltage Limits (For Advanced Users)
Setting voltage limits can help control CPU power consumption and thermal output, although this is an advanced setting that requires caution.
- Locate CPU Voltage Settings: In the CPU Configuration or Voltage Control section, locate settings labeled CPU Voltage or Core Voltage.
- Set a Lower Voltage: Carefully reduce the voltage limit to a stable level. Note that lowering voltage too much can cause instability, so proceed with caution and test for stability.
- Save and Exit: Apply the settings and monitor system stability within Windows 11.
Setting voltage limits in combination with a BIOS CPU frequency limit Windows 11 compatibility configuration ensures a balanced approach to energy efficiency and stable performance.
Benefits of Setting CPU Frequency Limits in BIOS for Windows 11
Configuring CPU frequency limits directly in BIOS offers several advantages:
- Hardware-Level Control: Adjusting frequency in BIOS applies settings before Windows 11 boots, making it an effective way to manage CPU power at the hardware level.
- Enhanced System Compatibility: Limiting CPU speed helps maintain stability for older systems or applications that may not require high performance.
- Better Resource Management: A well-tuned CPU frequency limit can help prevent overheating, battery drain, and throttling, enhancing the overall efficiency of your Windows 11 experience.
FAQs
Setting a CPU frequency limit in BIOS allows you to manage CPU performance at the hardware level, improving power efficiency, reducing heat, and ensuring stability. This approach can be useful for prolonging battery life or managing temperatures in Windows 11.
Yes, it’s safe to adjust CPU frequency in BIOS, as long as you make moderate changes and test your settings. Lowering CPU frequency won’t harm your hardware, but excessive changes may lead to performance issues if not tested carefully.
Yes, you can easily reset BIOS to default settings if you encounter issues. Most BIOS interfaces offer a Load Default Settings or Reset to Defaults option, allowing you to revert any changes you’ve made.
Yes, lowering CPU frequency can reduce power consumption and extend battery life on laptops running Windows 11. This adjustment is especially effective for lightweight tasks and general use.
No, while BIOS offers hardware-level control, you can also adjust CPU frequency within Windows 11 through Power Options and third-party software. However, BIOS adjustments apply before Windows boots, making them more consistent for system-wide settings.