Uncategorized
Schedule Compression Secrets: Slash Project Timelines by 30%
In today’s fast-paced environment, reducing project timelines without sacrificing quality is a valuable skill. When deadlines are tight, schedule compression techniques allow project managers to deliver results faster. Microsoft Project’s tools for critical path optimization and schedule compression tips provide powerful ways to shorten timelines by streamlining tasks, optimizing resources, and addressing bottlenecks. This guide covers advanced techniques that certified Project professionals use to compress schedules effectively, improve efficiency, and meet demanding deadlines.
Table of contents
- Why Microsoft Project Critical Path Optimization and Schedule Compression Tips Matter
- Getting Started with Critical Path Optimization
- Key Schedule Compression Techniques
- Advanced Microsoft Project Techniques for Schedule Compression
- Learn Expert Techniques for Optimizing Critical Paths and Compressing Project Schedules
Why Microsoft Project Critical Path Optimization and Schedule Compression Tips Matter
Critical path optimization and schedule compression techniques allow project managers to shorten timelines, save on costs, and enhance productivity. Microsoft Project critical path optimization and schedule compression tips help ensure that every task is necessary, well-scheduled, and resource-efficient, allowing for significant timeline reductions.
Using these techniques, you can:
- Eliminate Task Bottlenecks: Streamline workflows to remove delays in key areas.
- Enhance Resource Utilization: Ensure resources are used effectively and reduce idle time.
- Increase Project Flexibility: Compress timelines to accommodate tighter schedules, improving delivery rates.
These strategies offer a structured approach to timeline management, ensuring high-quality project completion even within challenging time constraints.
Getting Started with Critical Path Optimization
The critical path is the sequence of tasks that directly impact the project’s end date. By optimizing the critical path, you can effectively reduce the project’s overall duration without affecting task dependencies.
1. Identify the Critical Path in Microsoft Project
Begin by identifying the critical path in Microsoft Project to understand which tasks are essential for project completion.
- Switch to Gantt Chart View:
In Microsoft Project, go to the Gantt Chart view. Under Format, select Critical Tasks to highlight the tasks on the critical path. These tasks are the ones that must be completed on time to avoid delaying the project. - Review Task Dependencies:
Examine the dependencies between critical path tasks. Microsoft Project uses these dependencies to determine the order and duration of tasks, providing insights into how schedule adjustments can impact timelines. - Prioritize Critical Tasks:
Since tasks on the critical path have the greatest impact on project duration, prioritize resources and focus on these tasks first. Ensuring that these tasks stay on track is key to optimizing the project timeline.
2. Analyze and Minimize Task Durations
Shortening the duration of critical tasks is one of the most direct ways to compress a project schedule.
- Set Realistic Task Durations:
Review task durations in Microsoft Project and assess if they can be realistically shortened. Look for opportunities to streamline activities by using more efficient methods, tools, or processes. - Apply Historical Data:
If similar tasks have been completed faster in previous projects, adjust task durations accordingly. Microsoft Project allows you to modify task durations, helping you achieve a realistic yet shorter timeline. - Use Time Tracking to Validate Durations:
Track time spent on each task to validate whether the estimated durations are accurate. This real-time monitoring allows you to make adjustments to keep tasks on track and avoid unnecessary delays.

Key Schedule Compression Techniques
Once the critical path is optimized, use specific schedule compression techniques in Microsoft Project to further reduce the overall project duration.
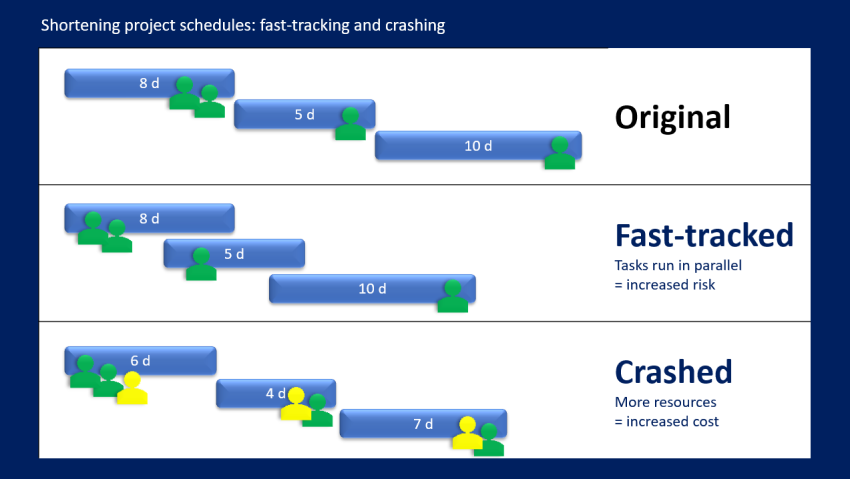
1. Fast Tracking: Overlap Sequential Tasks
Fast tracking involves performing certain tasks simultaneously rather than sequentially, reducing the timeline but potentially increasing risk.
- Identify Fast-Trackable Tasks:
Review the critical path to identify tasks that can overlap without causing resource conflicts. Tasks like Testing and Documentation might be conducted in parallel, as long as resources can manage both. - Adjust Task Dependencies in Microsoft Project:
In the Task Information window, change dependencies from Finish-to-Start (FS) to Start-to-Start (SS) to allow tasks to begin concurrently. This adjustment enables parallel work while preserving task relationships. - Monitor for Risks and Adjust as Needed:
Fast tracking can introduce risks due to overlapping tasks, so monitor progress closely. Use Microsoft Project’s tracking features to watch for delays or issues that may arise from overlapping activities.
2. Crashing: Allocate Additional Resources to Shorten Task Durations
Crashing involves adding extra resources to critical path tasks to complete them faster, reducing the project timeline.
- Identify High-Impact Tasks for Crashing:
Pinpoint tasks on the critical path that could be completed faster with additional resources. For instance, allocating more developers to a complex coding task might shorten its duration significantly. - Adjust Resource Allocations in Microsoft Project:
In the Resource Sheet, assign additional resources to high-impact tasks. Microsoft Project automatically recalculates task duration based on the new resource levels, allowing you to see the compressed timeline. - Balance Cost vs. Benefit:
Crashing can increase project costs, so weigh the benefit of timeline reduction against the additional expenses. Evaluate whether the compressed timeline justifies the increased resource costs.
3. Eliminate Non-Critical Tasks and Reduce Scope
When timelines are tight, consider reducing project scope by eliminating non-critical tasks that do not directly contribute to project goals.
- Identify Low-Priority Tasks:
Review the task list and look for tasks that do not impact the critical path. These may include optional features or administrative tasks that can be postponed or eliminated. - Reduce Scope Where Possible:
Collaborate with stakeholders to adjust project scope if necessary. In Microsoft Project, mark low-priority tasks as On Hold or remove them from the timeline to streamline the project schedule. - Monitor for Scope Creep:
Schedule compression can lead to scope creep if new tasks are added mid-project. Use Microsoft Project’s tracking tools to ensure that only essential tasks are included, maintaining focus on project goals.
Advanced Microsoft Project Techniques for Schedule Compression
To achieve even greater schedule compression, leverage Microsoft Project’s advanced features for managing resources, dependencies, and task tracking.
1. Optimize Resource Allocation Across the Project
Efficient resource allocation ensures that high-priority tasks on the critical path are completed without delays.
- Use Resource Leveling:
In Microsoft Project, apply Resource Leveling to optimize resource allocation. Resource leveling adjusts task schedules to resolve conflicts, ensuring that resources are fully utilized without overloading team members. - Allocate High-Impact Resources to Critical Tasks First:
Assign experienced or specialized resources to critical path tasks to improve task completion speed and quality. - Monitor Resource Costs in Microsoft Project:
Use the Cost Table in Microsoft Project to monitor resource costs and avoid budget overruns while reallocating resources to speed up the timeline.
2. Use Lag and Lead Time for Task Flexibility
Adjusting lag and lead time between tasks provides flexibility in scheduling and can reduce overall project duration.
- Add Lead Time to Overlapping Tasks:
Lead time allows successor tasks to begin before their predecessors are complete. For example, start Documentation during the final phase of Testing by adding lead time, allowing the project to move faster. - Apply Lag Time to Reduce Task Delays:
In cases where delays between tasks are necessary but can be shortened, reduce lag time to bring tasks closer together. Adjusting lag time in Microsoft Project compresses the timeline without changing task order. - Track Lead and Lag Adjustments in Critical Path View:
Monitor adjustments using the Critical Path view to ensure that reducing lag or adding lead time positively impacts the project timeline.
3. Utilize Baselines to Track Schedule Compression Progress
Baselines provide a point of reference for tracking progress and evaluating the success of compression efforts.
- Set Initial Baselines in Microsoft Project:
Save an initial baseline to capture the original timeline and schedule. This baseline acts as a benchmark against which compressed timelines are measured. - Compare Baseline to Current Timeline Regularly:
Use Microsoft Project’s Tracking Gantt view to compare the baseline with the current schedule. This comparison shows the impact of compression techniques, highlighting improvements and areas for further adjustment. - Update Baselines as Necessary:
If the schedule changes significantly due to compression efforts, save a new baseline to reflect the latest timeline. Updating baselines provides a clear picture of timeline adjustments over the project lifecycle.
Learn Expert Techniques for Optimizing Critical Paths and Compressing Project Schedules
Mastering Microsoft Project critical path optimization and schedule compression tips allows project managers to deliver projects faster without sacrificing quality or exceeding budgets.
Streamline Timelines with Fast Tracking and Crashing
By overlapping tasks and allocating additional resources to high-priority items, project managers can compress schedules effectively, reducing project timelines by up to 30% while staying within resource and budget constraints.
Use Baselines and Tracking Tools for Better Visibility
Setting baselines and tracking progress in Microsoft Project ensures that schedule compression efforts are measurable, allowing project managers to monitor the impact of adjustments in real-time and make informed decisions.
FAQs
In the Gantt Chart view, go to the Format tab and select Critical Tasks. Microsoft Project highlights tasks on the critical path, showing which tasks impact the project’s end date.
Fast tracking involves overlapping tasks to reduce project duration, while crashing involves adding extra resources to critical path tasks to complete them faster. Both techniques aim to compress timelines, but fast tracking may increase risk.
Yes, use Microsoft Project’s Cost Table to track resource costs as you reallocate resources or shorten task durations. This feature helps ensure schedule compression efforts
stay within budget.
In the Task Information window, adjust the Predecessors field to add lead or lag time. Lead time allows tasks to overlap, while lag time introduces a delay between tasks, providing flexibility in scheduling.
Use Microsoft Project’s Tracking Gantt view to compare the current schedule to the baseline. This view helps project managers monitor improvements, identify areas for further compression, and track the project’s overall timeline.