Uncategorized
Bulletproof Backup Strategy for Windows 11 Ransomware Defense
As ransomware threats grow increasingly sophisticated, having a robust backup strategy is essential to protect critical data and ensure quick recovery. Windows 11 ransomware recovery backup strategy offers several techniques to secure your data against ransomware, such as air-gapped backups, versioning, and automated recovery procedures. This guide will take you through the key steps to creating an impenetrable backup system, helping you avoid costly downtime and data loss.
Why a Strong Backup Strategy is Essential for Ransomware Defense
Ransomware attacks often target files and folders, encrypting them and holding them hostage until a ransom is paid. But even if you pay, there is no guarantee that your files will be decrypted. Having a Windows 11 ransomware recovery backup strategy means you can quickly restore your data, minimizing disruption and eliminating the need to negotiate with attackers. A comprehensive backup plan not only reduces risk but also adds an essential layer of resilience to your business operations.
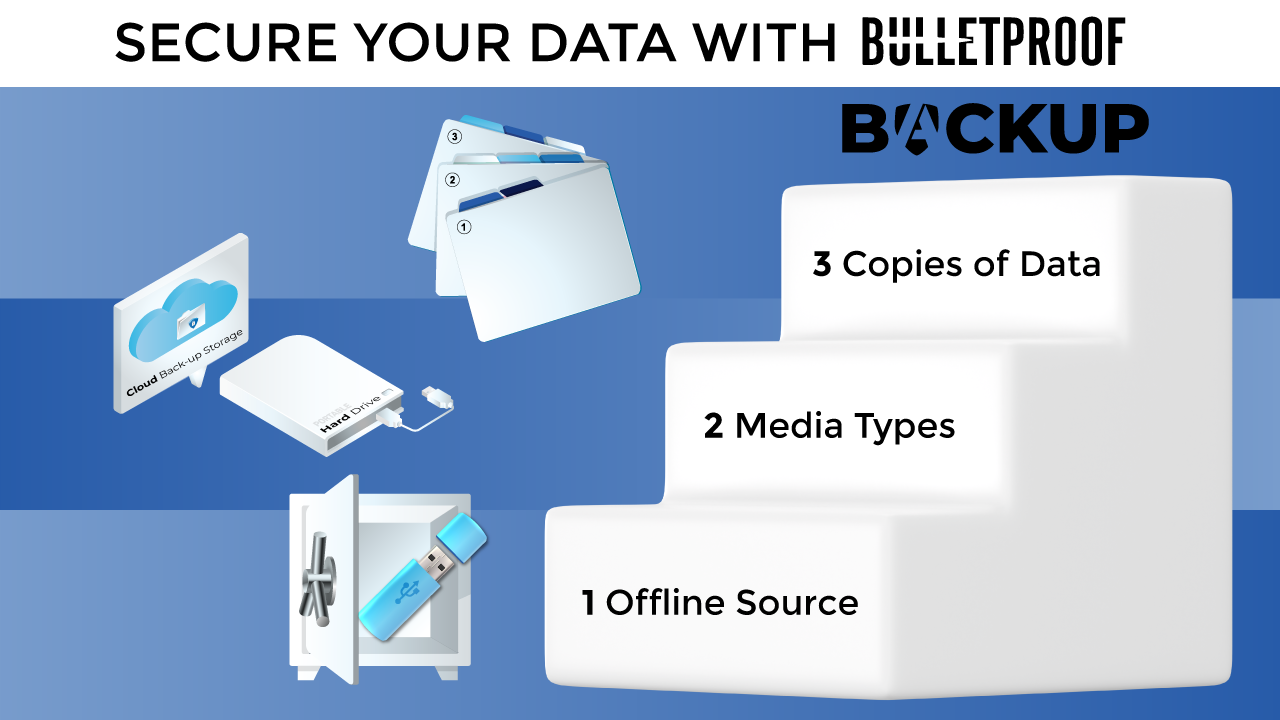
Core Components of a Bulletproof Backup Strategy
An effective Windows 11 backup strategy for ransomware defense includes several core components. From air-gapped backups to file versioning, these elements work together to create a multi-layered approach that ensures data recovery even after a ransomware attack.
1. Air-Gapped Backups: Physical and Logical Separation
An air-gapped backup is physically or logically isolated from the network, making it inaccessible to malware and ransomware. This type of backup is a critical part of a Windows 11 ransomware recovery backup strategy as it prevents ransomware from reaching your backup files.
Types of Air-Gapped Backups
- Physical Air-Gap: Store backup data on a device that is disconnected from the network, such as an external hard drive or offline server.
- Logical Air-Gap: Create a cloud-based backup with restricted network access, isolating it from your main network.
Implementing Air-Gapped Backups
- Set Up an External Drive: Use an external drive for backups and disconnect it after each backup cycle. This drive should only be connected to the system during backup processes.
- Leverage Cloud Storage: Opt for cloud providers that offer air-gapped storage, such as immutable backups. This setup restricts access to specific accounts or users, protecting backups from network-based attacks.
2. Versioned Backups: Protect Against Data Corruption
Versioning allows you to keep multiple copies or “versions” of your files. If ransomware encrypts or corrupts your data, you can easily roll back to a clean version. In Windows 11, File History and OneDrive versioning enable you to revert to previous file versions, protecting you against accidental or malicious modifications.
How to Set Up Versioned Backups in Windows 11
- Enable File History: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Backup and select Add a drive. Choose a drive to save backup versions of your files.
- Use OneDrive Versioning: If you use OneDrive, go to OneDrive > Settings > Manage Storage, and enable versioning. This will save multiple versions of your files, making it easy to revert to a previous version if ransomware alters your files.
Benefits of Versioning: Versioned backups provide a snapshot of your files at specific points in time, ensuring that even if a ransomware attack corrupts your current files, you can restore previous, unaffected versions.
3. Automated Backup Scheduling: Consistent Protection
Automating backups reduces the risk of human error and ensures that all data is consistently protected. Windows 11 offers scheduling options for File History and can also integrate with third-party backup solutions for even more control.
Setting Up Automated Backups in Windows 11
- File History Scheduling: In Settings > Update & Security > Backup, enable File History and set the frequency (e.g., every hour, daily).
- Third-Party Backup Tools: Use tools like Acronis True Image or Macrium Reflect to schedule and automate full-system backups. These solutions offer more customization and frequency control.
Advantages of Automation: By automating backups, you create a continuous backup process that ensures new and modified files are protected without manual intervention. This consistency is key in a ransomware defense strategy.
4. Offsite Backup Storage: Protect Against Physical Damage and Localized Attacks
Offsite backups ensure that you have copies of your data stored in a separate physical location. If a ransomware attack or physical disaster compromises your main system, offsite backups allow for recovery.
Options for Offsite Backups
- Cloud-Based Storage: Cloud storage providers like Microsoft Azure and Amazon S3 offer highly secure offsite backup options.
- Dedicated Offsite Server: For businesses with higher storage needs, setting up a dedicated offsite server provides an additional layer of security.
Benefits: Offsite backups protect against natural disasters, theft, and localized attacks, making them essential in a resilient Windows 11 ransomware recovery backup strategy.

Advanced Techniques for Ransomware Defense
Data Encryption for Backup Files
Encrypting your backup data ensures that even if attackers gain access, they cannot read or use the information. Windows 11 offers BitLocker for device encryption, and many backup tools include encryption options for additional security.
- Enable BitLocker on Backup Drives: Go to Settings > System > Device Security and enable BitLocker Drive Encryption for external backup drives.
- Use Encrypted Cloud Storage: Many cloud providers offer built-in encryption. Choose a service that encrypts your data both at rest and in transit.
Ransomware Detection and Recovery
Advanced backup solutions offer ransomware detection that can monitor your system for suspicious behavior, such as rapid file encryption, and automatically alert you.
- Enable Windows Defender Real-Time Protection: In Windows Security > Virus & Threat Protection, activate Real-Time Protection to monitor for suspicious activity.
- Use Third-Party Detection Tools: Programs like Malwarebytes and Acronis Active Protection provide ransomware detection and can automatically stop attacks.
Regular Testing of Backup Integrity and Recovery Procedures
A backup strategy is only as effective as its ability to restore data accurately. Regularly test your backup files to ensure they can be restored fully and without corruption.
- Conduct Test Restorations: At regular intervals, perform test restorations to verify that backup files are accessible and intact.
- Simulate Recovery Scenarios: Run simulations for potential ransomware events to gauge how quickly and effectively you can restore operations from backups.
Setting Up a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)
A disaster recovery plan complements your backup strategy by outlining specific steps for responding to ransomware attacks and restoring operations.
Key Elements of a DRP for Ransomware Defense
- Backup Schedule: Define a schedule that includes daily incremental backups and weekly full backups.
- Access Controls: Limit backup access to trusted personnel only and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Recovery Steps: Detail the process for restoring backups, including software requirements and recovery timelines.
A DRP not only speeds up the recovery process but also reduces downtime by ensuring all stakeholders know the protocol in the event of an attack.
FAQs
Air-gapped backups are isolated from the network, making them inaccessible to ransomware. This physical or logical separation prevents ransomware from reaching your backup files.
Versioning keeps multiple copies of files, allowing you to restore previous versions if ransomware encrypts or corrupts your data. This feature is available through File History and OneDrive.
Automated backups ensure continuous data protection without manual intervention, reducing the risk of missed files or outdated backups in the event of a ransomware attack.
Yes, combining local and cloud storage provides a layered approach. Local backups enable quick recovery, while cloud storage offers secure offsite redundancy.
BitLocker encrypts backup drives, preventing unauthorized access. If ransomware attempts to access encrypted data, it remains unreadable.