Uncategorized
Adjust RAM Speed in BIOS Settings Windows 11 with XMP for Peak Performance
If you’re looking to elevate your PC’s performance, maximizing your RAM speed is an essential step. By adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11 and enabling XMP (Extreme Memory Profile), you can unlock the true potential of your memory modules. This configuration enhances system responsiveness, speeds up data processing, and optimizes multitasking capabilities. However, configuring RAM settings requires a careful approach to maintain system stability and avoid hardware issues.
This blog post will guide you through the process of adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11 using XMP profiles, explain key memory settings, and highlight best practices for stable and optimized performance.
Table of contents
- Understanding XMP and Its Role in Optimizing RAM Performance
- Benefits of Adjusting RAM Speed in BIOS Settings in Windows 11
- How to Access BIOS and Enable XMP in Windows 11
- Advanced RAM Configuration in BIOS
- Testing RAM Stability After Adjustment
- Maximizing RAM Performance Safely
- Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Tips
- FAQs
Understanding XMP and Its Role in Optimizing RAM Performance
Extreme Memory Profile (XMP) is an Intel-developed technology embedded in many RAM modules. XMP provides predefined profiles for RAM that adjust frequency, voltage, and timing settings, allowing you to maximize RAM performance with minimal effort. When you enable XMP in your BIOS, your RAM operates at speeds it was designed for rather than default (often lower) speeds, offering a significant performance boost without manual configuration.
Benefits of Adjusting RAM Speed in BIOS Settings in Windows 11
Configuring XMP and adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11 can offer a variety of benefits, including:
- Increased Data Transfer Rates: Higher RAM speeds reduce the time taken to move data between memory and the CPU, enhancing responsiveness and processing power.
- Better Multitasking: Faster RAM helps handle multiple tasks more efficiently, making it ideal for users running multiple applications or memory-intensive software.
- Improved Gaming Performance: For gamers, increased RAM speed reduces stuttering, enhances frame rates, and smooths gameplay.
Now, let’s dive into how to enable XMP in BIOS and make RAM adjustments safely.
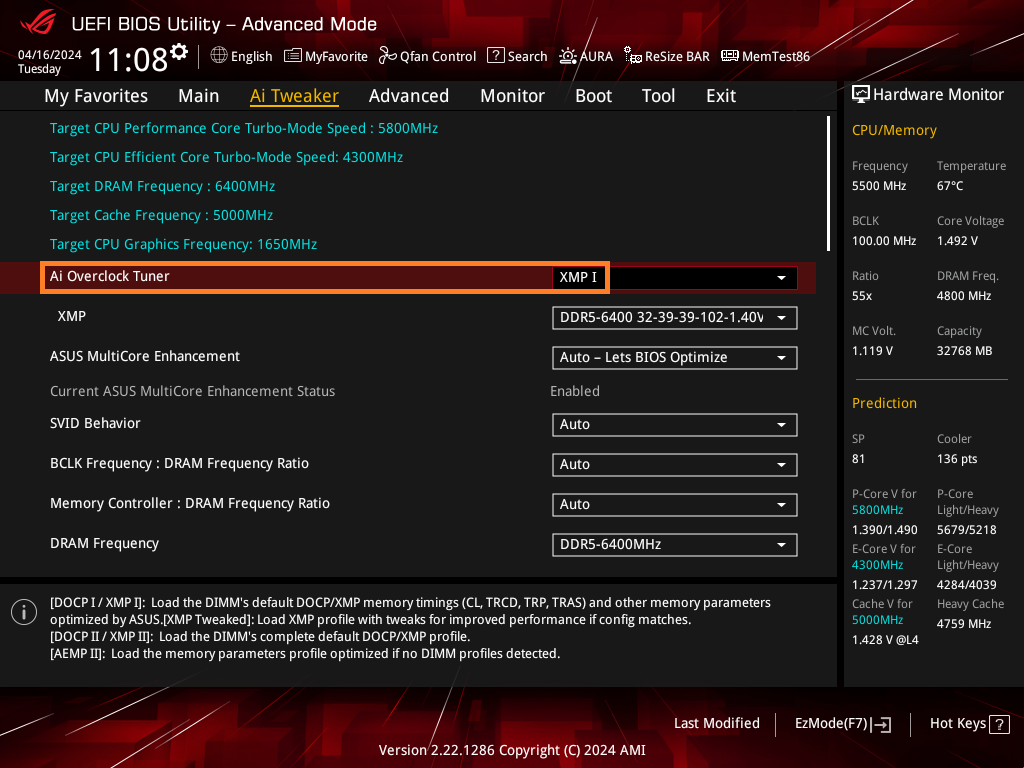
How to Access BIOS and Enable XMP in Windows 11
Step 1: Accessing BIOS in Windows 11
To adjust RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11, you first need to access the BIOS interface. Here’s how:
- Open Settings: Click on the Start menu, select Settings, and navigate to System.
- Go to Recovery Options: Under System, select Recovery and then click Restart now under Advanced startup.
- Choose Troubleshoot: After restarting, select Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, and finally UEFI Firmware Settings. Click Restart to boot into BIOS.
Alternatively, if you’re restarting your PC, press the BIOS access key specific to your motherboard (often DEL, F2, or ESC) during boot-up.
Step 2: Enable XMP in BIOS
Once in the BIOS menu, follow these steps to enable XMP:
- Locate the XMP Option: XMP settings are typically found under tabs like Extreme Memory Profile, Memory, or Overclocking. Some BIOS interfaces may label it as D.O.C.P. (Direct Overclock Profile) on AMD motherboards.
- Select XMP Profile: Choose from available XMP profiles (usually XMP Profile 1 or Profile 2). Profile 1 is often a standard setting, while Profile 2 may offer a slightly higher frequency.
- Save and Exit: Once you’ve selected an XMP profile, save changes and exit the BIOS. Your system will reboot, applying the new RAM speed settings.
Note: BIOS layouts and settings may vary by manufacturer. Consult your motherboard manual for specific instructions.
Advanced RAM Configuration in BIOS
Enabling XMP typically optimizes RAM speed without needing manual adjustments. However, advanced users may wish to refine memory timings and voltages further to maximize stability and performance. Below are the most crucial settings when adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11.
1. Memory Frequency
The memory frequency setting controls your RAM speed. While XMP profiles will usually set this automatically, you can make further adjustments if your RAM and motherboard support higher frequencies. Higher frequencies translate to faster data transfer rates but may impact stability if not configured properly.
- Adjusting Memory Frequency: In the Memory or Overclocking tab, you can select a frequency (e.g., 3000 MHz, 3200 MHz, etc.) compatible with your RAM.
2. Memory Timing
Memory timings refer to the delay cycles required for data processing. Lower timing numbers usually indicate faster RAM performance, but reducing timings too much can destabilize your system. Common timing values include CAS Latency (CL), tRCD, tRP, and tRAS.
- Adjusting Memory Timing: Timings are typically grouped, so you can adjust values together (e.g., setting 16-18-18-38). Lower these values gradually and test system stability after each adjustment.
3. DRAM Voltage
DRAM voltage powers the memory modules, and higher voltages can improve stability for overclocked RAM. However, excessive voltage increases heat output, which may harm the memory over time.
- Setting DRAM Voltage: In the BIOS, adjust DRAM voltage settings only incrementally (e.g., increase by 0.01V at a time). Ensure your RAM can handle the voltage levels you set, as exceeding safe thresholds can damage the hardware.
Testing RAM Stability After Adjustment
After adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11 and enabling XMP, it’s essential to verify stability. Use the following methods to ensure that your system runs reliably at its new configuration:
- Run MemTest86: MemTest86 is a popular utility for testing RAM stability. Bootable from a USB, it thoroughly checks for memory errors and instability.
- Use Prime95 Blend Test: Prime95 offers a Blend Test option that stresses RAM to verify system stability under heavy loads.
- Monitor Temperatures: Higher speeds and voltages can lead to increased temperatures. Use software like HWMonitor to track RAM temperatures, and ensure they remain within safe limits (generally below 85°C for DRAM).
Tip: Test for stability after each incremental change. Running each test for a few hours can confirm whether your settings are reliable.
Maximizing RAM Performance Safely
When adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11, follow these best practices to maintain optimal performance and system stability:
- Choose the Right XMP Profile: XMP profiles are pre-tested and designed for specific RAM modules. Select a profile appropriate for your memory model.
- Avoid Excessive Voltage: Stay within the safe voltage range recommended by your RAM manufacturer to avoid overheating and potential damage.
- Use Incremental Changes: Small adjustments to frequency, timings, and voltage are safer and allow you to revert easily if instability occurs.
- Monitor Temperatures: Overclocked memory can generate more heat, so ensure your PC’s cooling system is adequate.

Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Tips
- System Fails to Boot: If your system fails to boot after adjusting RAM speed, return to the BIOS and revert to default or lower settings.
- Frequent Crashes or Errors: Unstable RAM configurations often cause system crashes or application errors. Reduce frequency or loosen timings if instability persists.
- High Temperatures: If you notice excessive heat, consider improving cooling or reducing DRAM voltage and frequency.
FAQs
Most modern RAM modules come with XMP support, which is often labeled on the packaging or in the product specifications. You can also check your motherboard’s manual for compatibility information.
No, enabling XMP does not void the warranty on most RAM modules, as XMP profiles are pre-approved settings created by the manufacturer. However, manually overclocking or exceeding recommended voltages may void the warranty.
Yes, while XMP is an Intel technology, most AMD motherboards support a similar feature known as D.O.C.P. (Direct Overclock Profile), allowing you to enable XMP-like profiles on AMD platforms.
Setting RAM speed higher than its rated frequency may lead to instability, data corruption, and potential hardware damage. Always follow manufacturer recommendations and test for stability when increasing frequency.
If your system becomes unstable, enter the BIOS and reset settings to Default or Auto for memory-related options. This will restore the original RAM configuration.
By adjusting RAM speed in BIOS settings in Windows 11 and enabling XMP profiles, you can unlock the full potential of your system’s memory, improving performance across various applications. Following these best practices will help you maintain a stable and optimized system, allowing you to make the most of your memory resources for a smooth and efficient computing experience.